Advanced technology radiology: Who among us hasn’t fantasized about possessing X-ray vision at some point in our lives? To be able to see things that the human eye is unable to be an amazing ability, to say the least. A superhero’s daydreams of seeing more than the human eye can take in have a lot more practical applicability than the fantasy world of a marvel comic teenager. When diagnosing a patient’s condition, medical practitioners frequently need to see into the patient’s body. Fortunately, diagnostic tests can do tasks that the human eye is unable to. Radiologic technicians utilize their “powers” to help save lives, but they don’t wear capes to do so.
Non-invasive diagnostic imaging allows doctors to see into the body without the need for surgery. Doctors can view how joints move, how internal organs work, and a lot more with these tests. Everything from verifying the existence of illness to assessing the severity of an injury may be accomplished using medical testing, including formulating a plan for future surgical operations.
The tests are carried out by radiologic technologists in collaboration with patients. What skills and knowledge are required of a radiologic technologist? According to the Society Of Radiologic Technologists, “anatomy, patient positioning, examination procedures, equipment protocols, radiation safety, radiation protection, and basic patient care” are all important. Even though it’s a lot of work, it may pay off in the long run.
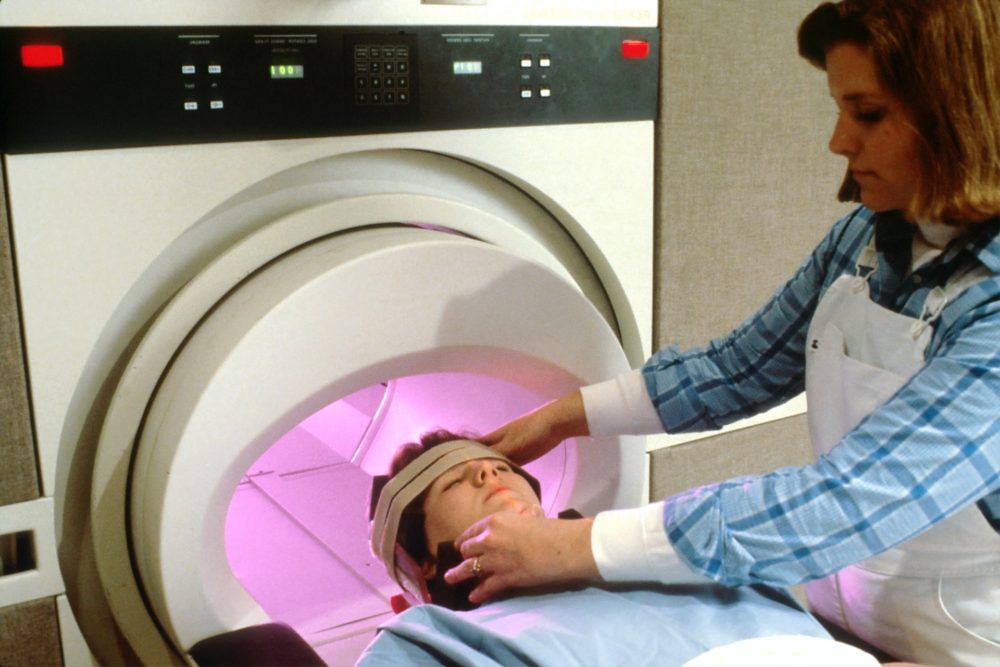
Frequently Performed Imaging Diagnosis Procedures: Advanced Technology Radiology
Do you know what you’ll be doing on a regular basis if you’ve received enough training? As a diagnostic imaging expert, you’ll likely help with the following seven operations.
X-Rays
In medical institutions, X-rays are the most often conducted diagnostic imaging exams. This broad phrase encompasses a wide range of specific types of X-rays. X-rays are used for a variety of purposes, including the diagnosis of pain, determining the degree of an injury, monitoring the course of illness, and assessing the effectiveness of therapy.
Small amounts of radiation are directed to certain parts of the body in order to get pictures using X-rays. An important first step is to ensure the patient also isn’t wearing any jewelry or clothing that might interfere with the picture quality. Once the patient is in the proper posture, the rest of the procedure may begin. It’s time to capture some images of what’s happening within the body now that everything is set up.
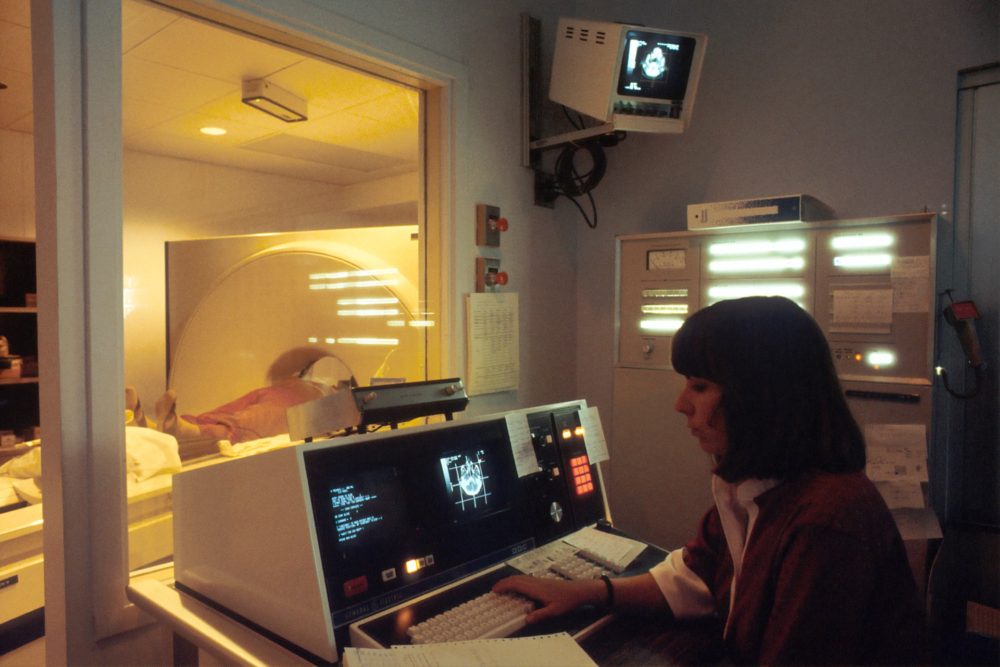
A Computed Tomography Scan
CT scans, also known as computed axial ct scans or CAT scans, provide medical professionals with images of the body in cross-section. There are several advantages to cross-sectional X-rays, which generate more accurate pictures than traditional ones. When an X-ray shows anything abnormal, a Computed tomography is often recommended.
As the patient moves through the scanner’s center, it creates a donut-shaped picture of their insides. In order to see what’s going on within the body during some examinations, the patient may be given an injection with contrast dye or an oral contrast dye. The technician places the patient just on the scanner bed and departs the room after everything is set up and ready. The technician runs the scanner from a control room, which takes the patient through the center at a leisurely pace.
Please fill out the form below to learn more about becoming a CT certified radiologist. Visit the Computerized Tomography Training website at Rasmussen College to find more about how Rasmussen can assist you with your career development.
MRI
Advanced technology radiology: Magnetic resonance imaging, sometimes known as an MRI, is another cross-sectional imaging technique. For detecting soft tissues including organs and tendons, MRIs are an excellent alternative to CAT scans. An MRI uses radio waves and magnetic fields instead of ionizing radiation, unlike a CAT scan. MRIs are regarded to be safer since they don’t involve radiation, and they also take way more time. In comparison to a CAT scan, an MRI may require up to 30 minutes or more depending on the process.

Are you interested in learning more about magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)? For further information, see the MRI Training section.
Mammography
In the fight against breast cancer, there are two kinds of mammograms: screening and diagnostic. First, screening mammography is done to look for abnormalities. Following the discovery of a lump or abnormal thickness in the breast, diagnostic mammography may be used to rule out cancer. In the battle against breast cancer, early diagnosis is critical.
If a screening and diagnostic exam have been conducted, the best practices used by technologists will be different. Each breast is photographed at least twice during a screening check. A technician will take a greater number of pictures during a diagnostic evaluation. Physicians may also analyze worrisome spots with the use of magnified photographs.
Ultrasound
An ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to produce pictures of the inside of the body. The soft tissues of the body, such as organs or arteries, are often examined with this technique. Ultrasounds are the preferred method of examining pregnant women since they do not utilize radiation.
How to get ready for an ultrasound depends on what you’re going to be looking at throughout the procedure. Fasting is required for all abdominal examinations, however, patients are permitted to ingest water. When patients are examined, a lubricant is sprayed on their skin. High-frequency sound waves are emitted by a transducer as it glides over the skin. A picture of what’s going on within the body is created by these sound waves
Fluorescence Microscopy
Fluoroscopy, on the other hand, is like seeing a movie of your body’s processes in action, whereas other tests are like taking still photos. As a result, fluoroscopy is able to display moving components of the body. Contrast dyes are often used in this treatment to demonstrate the path the dyes go through the body. This is all taking place as an X-ray beam transmits signals to something like a monitor. In addition to bones, joints, organs, and vasculature, fluoroscopies may be used to examine soft tissue, such as skin, muscle, and tendons. Fluoroscopy is often used in blood flow tests.
A patient is placed on an exam table by a technician first. Fluoroscopy, unlike many other tests, does not need the patient to remain still. Instead, the technician may urge the patient to move throughout the procedure in order to see how the body responds to movement. Contrast dye injections into the body may be uncomfortable, thus technicians may need to provide comfort measures. Fluoroscopy alone is not painful.
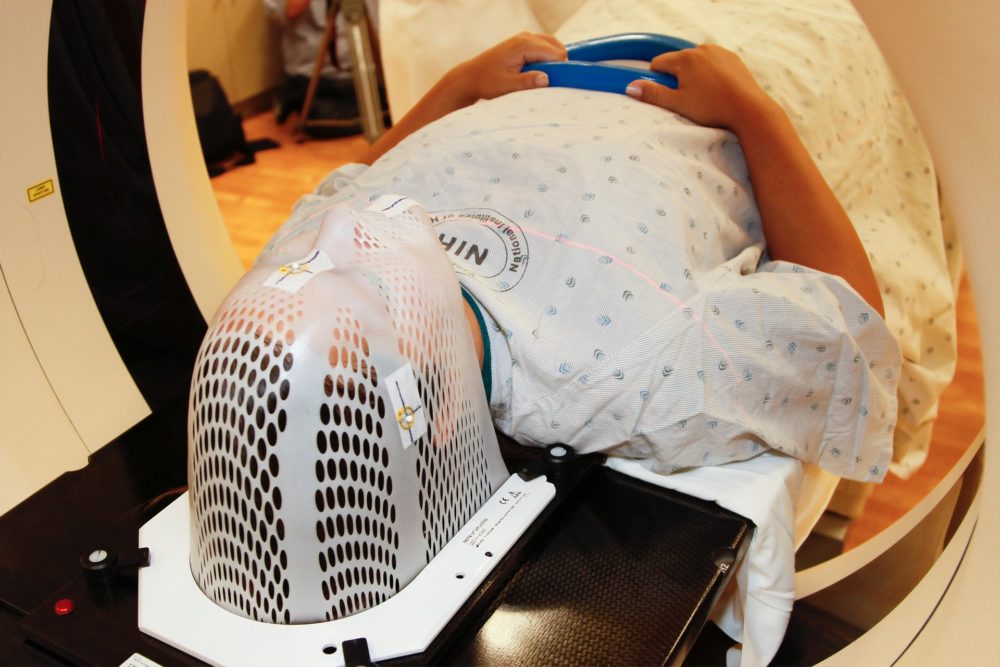
Pet Scans
Positron emission tomography (PET) scans are like illness detection in the body since they identify abnormalities in cells. Radioactive tracers are injected into the patient during the surgery. Problems that could normally go unnoticed until they worsen are discovered using tracers and PET scanning.
Tracers may be administered in one of three methods, depending on the procedure: intravenously, by inhalation of gas, or orally, via a particular combination. An hour-long wait is required since it takes time for tracers to go through the body. An O-shaped machine rotates the patient’s table while they wait for the procedure to begin. Instructing the patient to remain still and hold one’s breath is the technologist’s primary responsibility.
 Hyper Automation
Hyper Automation
When technology is used to automate a task, it is called hyper-automation. It is now possible to automate tasks that formerly needed people by using cutting-edge technology like machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI). It is possible to automate several tools using this technology, which is critical since no tool can totally replace a person. To achieve hyper-automation, a number of tools must be used together.
The Following Are Included In This Combination:
- Automation by robots (RPA).
- The use of artificial intelligence.
- Software for the intelligent administration of business (iBPMS).
- Hyperautomation’s ultimate objective is to increase the number of choices made by AI.
Machine Learning And Artificial Intelligence
There are new diagnostic tools that can be taught to interpret X-rays and tissue samples because of the combination between AI and ML. The use of this cutting-edge equipment by radiologists helps speed up patient diagnosis. Improved Diagnosis with the Help of AI
Radiologists will be happy to lend patients a more accurate diagnosis because of AI’s capacity to automate tedious chores and aid with selecting cases or secondary readings based on tumor detection. For these goals, AI help is already being used by a number of Swedish pathology and advanced technology radiology departments.
Artificial Intelligence (Ai) Will Permit Ongoing Training.
As a result of artificial intelligence, doctors and nurses will be able to keep up their education on a constant basis. The majority of the time, this is done through creating feedback loops. There are a number of ways in which radiologists may access earlier cases in order to learn more about the pathology and/or operation results.
Artificial Intelligence Security
Nearly four out of every five cybersecurity breaches in the healthcare business happened in 2019. The cost of healthcare data breaches in 2019 is expected to exceed $4 billion by the end of the year, and it is expected to rise even more in 2020.
Ninety-six percent of the IT experts polled by Black Book Consumer Research believe that data attackers are surpassing medical institutions. Consequently, this leaves providers open to cyberattacks. According to study results, more than half of all assaults in 2019 were the result of foreign hacking.
Radiologists must deploy an AI secure system that can recognize patterns and secure data in order to realize the advantages of hyper-automation, but it also has its drawbacks.
An artificial intelligence protection system’s most important views include:
Training data, ML models, and training pipelines for AI-powered systems must be safeguarded.
Machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) may be used together to increase security defenses by analyzing trends, identifying potential threats, and automating certain cybersecurity processes.
Protecting the data against illicit uses of artificial intelligence.
Automatic resizing of space
Currently, several pilots of artificial intelligence-aided workflow management are being tested, while others are still under development.
The radiologist’s workload must be taken into account when determining the number of examinations that may be automatically redistributed.
Automated exam scheduling based on time like day, department, specialty, and other variables.
The advanced technology radiology examinations and reading capacity are automatically balanced.
Assign studies depending on the radiologist’s availability, location, subspecialties, time daytime, and other variables.
Artificial intelligence will initially evaluate particular examinations. In certain cases, the kind of test and the person making the request determine which examinations are administered. It is possible to seek AI-assisted pre-analysis in the event of a pulmonary embolism test.
Configuring and monitoring service-level agreements (SLA) tests by prioritizing radiologists’ reading queues and establishing adjustable deadlines.
Data will be used and used by AI-based workflow systems in the future, allowing them to aid in operations management. Some examples include the ability to identify bottlenecks. Radiologists who are available will be prioritized based on that information, resulting in shorter wait times and more efficient patient treatment. When radiologists begin using an Enterprise workflow orchestration way early on, they have a leg up on the competition.
The Pathology Department collaborates with other departments at the university
Radiologists have the potential to take lead in the administration of cross-disciplinary workflows in order to deliver the best possible care for patients. When it comes to integrated diagnostics, radiologists can have no trouble embracing digital technology since they are one of the most IT-savvy healthcare professionals. Pathologists are now analyzing pictures digitally, paving the way for interdisciplinary cooperation.
Stereotactic Breast Biopsies
For the purpose of diagnosing cancer or other diseases, breast tissue is removed and examined.
Stereotactic, ultrasound-guided, MRI-guided and excisional breast biopsies are only a few of the options for breast biopsies. When it comes to removing cancerous tissue from a woman’s breast, stereotactic breast biopsy is a great option.
Procedures For Doing The Test.
From the waist down, you must remove all of your clothing. You are awake throughout the biopsy.
In order to perform a biopsy, you will also most likely be required to lay on your back. The breast that has been biopsied hangs from a tabletop opening. The doctor conducts the biopsy underneath the table. A stereotactic breast biopsy may be performed while you are seated upright in certain instances.
The Biopsy Is Carried Out As Follows:
In order to prevent infection, the healthcare expert first sanitizes this region of your breast. An injectable anesthetic is administered.
During the surgery, the breast is held in place by pressing it down. In order to get an accurate biopsy, you must remain perfectly motionless throughout the procedure.
A very little incision is made on your breast by the doctor over the suspected tumor’s location.
With the use of an automated tool or device, a needle and sheath is directed to the precise site of the abnormality being treated. A number of breast tissue samples are obtained.
During the biopsy, a tiny metal clip may indeed be inserted into the breast. Using the clip, a surgical biopsy may be performed if necessary.
Both of the following methods is used to do the biopsy:
- A needle with a hollow core
- Instrument drove by vacuum
- Vacuum as well as needle-driven apparatus
- About an hour and a half are typical for the operation. For the x-rays, this comprises the time required. Only a few minutes are required for the actual biopsy procedure.
The needle is withdrawn once the piece of tissue has been collected. To halt any bleeding, ice & pressure are administered to the area. Any remaining liquids will be absorbed by a bandage. There’s no need for stitches. Over any wound, adhesion strips may be applied.
Biopsy
When a sample of tissue is taken for testing, it is known as a biopsy.
- Procedures for doing the test.
- Biopsies come in a variety of forms.
When a needle biopsy was performed, a local anesthetic is used for the procedure. Both kinds exist.
A syringe and a tiny needle are used in fine-needle aspiration. Tissue tissue is removed in very minute quantities.
That used a hollow needle linked to a spring-loaded instrument, a core biopsy extracts slivers of tissue.
Multiple passes through the tissue are required with any form of needle biopsy. The needle is used by the doctor to take a sample of tissue. The most common methods for doing needle biopsies are CT scans, MRIs, mammograms, and ultrasounds. These imaging devices aid the physician in locating the correct location.
Local or general anesthesia may be used during an open biopsy. As a result, you will be in a state of deep relaxation (sedation or sleep) throughout the treatment. The procedure is carried out in the operating room of a medical facility. Cuts are made in the afflicted location as well as the tissue is extracted by the surgeon.
Smaller surgical incisions are required for a laparoscopic biopsy compared to an open biopsy. One or more instruments (such as a laparoscope) may be inserted. The laparoscope helps the surgeon find the proper area to obtain a sample.
It is possible to do a melanoma biopsy by removing a tiny sample of skin and examining it. Tests on the skin seek illnesses or skin disorders.
 Advanced Technology Radiology: Carotid Artery Angioplasty And Stenting
Advanced Technology Radiology: Carotid Artery Angioplasty And Stenting
Carotids supply blood to the heart that provides blood to the brain and face. Both of your neck’s carotid arteries are located on either side of your head.
Plaque, a kind of fatty substance, may obstruct the flow of blood in this artery. Carotid artery stenosis refers to a partial occlusion (narrowing). The blood flow to your brain might be compromised if you have a blockage in the carotid artery. In rare cases, a portion of a plaque might dislodge from the rest of the artery and obstruct another one. Insufficient blood flow to the brain may result in a stroke.
Treatment for a narrowed or obstructed carotid artery may be accomplished via the use of two different methods. These are the ones I’d like to point out:
- Plaque removal with surgery (endarterectomy)
- Carotid stenting and angioplasty
- An incision is made in the carotid artery to perform a carotid angioplasty (CAS).
After administering an anesthetic, your doctor will create a surgical incision in your groin. You’ll also be given medication to help you feel more comfortable.
A flexible tube (catheter) is inserted into an artery via the incision made by the surgeon. Your carotid artery is gently pushed up your neck to the occlusion. The catheter is guided to the proper location using moving x-ray images (fluoroscopy).
The surgeon will next insert a wire into the catheter and guide it to the source of the obstruction. Using a catheter with such a tiny balloon on the end, the obstruction will be removed. The balloon is then blown to its full height.
Your artery is pressed against the inside of the balloon. As a result, more blood may flow into your brain. A stent (a wire tube) might be inserted into the obstructed space. At the very same time as that of the balloon catheter, the stent is implanted. The balloon causes it to expand. Because the stent is still in place, it helps to maintain the vessel open.
Afterward, the balloon is removed by the surgeon.
In today’s world, radiologists are more important than ever.
Radiologists were understandably frightened by all the chatter about artificial intelligence and robotics. Even for the most modern automation technologies, we now understand that is not the case.
There is still a need for radiologists, and they play a critical role in clinical treatment and patient involvement. As a healthcare provider, you need to make use of all of the technology and analytics information that you have at your disposal, not only for your operations but for the benefit of your customers as well. Think of it as translating raw data for the general public.
The importance of the area may be seen from this perspective, making it a desirable career path both now and into the. Indeed, being a radiologist has several advantages. Despite the fact that many contemporary operations are now automated, this frees up so much time for clinical treatment or patient encounters, which is why human workers are still required.
It’s easier for people to understand what’s going on with their health when they have a radiologist to turn to.
Radiologists’ Roles Will Continue To Expand.
Advanced technology radiology: Moreover, the radiologist’s position will continue to grow in importance over time. It’s hard to believe, but automation or machine learning technology has the ability to cover all of the tedious labor that most technicians are responsible for. Imagine not having to sift through charts, graphics, and data anymore! The data is still there, and it still has to be provided to patients and indeed the doctors who assist them, but it is now collected more quickly and with more precision.
Cloud computing with smart, linked technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT) provides real-time data as another component of this. A radiologist’s ability to interpret, translate and suggestions based on digital material is almost instantaneous.
As a result, these health professionals now have much more clout and are able to contribute in more ways. Radiologists may have a greater impact on a patient’s care team by participating for longer periods of time.
Wearable Diagnostic Devices Are Becoming More Popular.
Medical experts can’t be with their patients 24 hours a day, whether they’re in a hospital or a clinic, or even if they’ve just had a fast checkup. Doctors may, however, keep tabs on their patients in real-time, particularly those who require it the most. Medical gadgets that are worn on the wrist, such as smartwatches or heart monitors, may be used to collect more detailed information about the user and their habits.
MEG wearable brain scanners, in particular, may have a significant influence on the way patients are examined and diagnosed in Radiology. There are a lot of low-cost gadgets out there that can deliver just as much information as some of the most costly machines.
 The Mobile Age Is Upon Us
The Mobile Age Is Upon Us
For the time being, FDA-approved medical imaging apps and mobile solutions are few and far between. To be sure, mobile technology can have a significant influence on imaging, diagnostics, and patient involvement in the next few years.
In addition, mobile is a very profitable platform since it is always-on and can be used from any location at any time. Think about mobile and classroom training for aspiring radiologists. You may also use OTA (over-the-air) screening or imaging. As a result of secure, zero-footprint communication methods, consulting is also available.
When It Comes To Radiology, The Future Is Bright.
There is no certainty that the patterns outlined here will continue in the future. If AI doesn’t have a major influence on the industry, or if mobile doesn’t take on, it’s certainly plausible. As far as I’m concerned, one thing is for sure: the advanced technology radiology sector will soon be transformed for the better.
Patients will be better cared for, new therapies will be available, and outdated procedures and operations would be brought into the 21st century. As a result, patient care will be more precise and efficient than ever before for field experts.
As dazzling as the negative areas of an X-Ray, radiology’s future is bright, too!



 Hyper Automation
Hyper Automation Advanced Technology Radiology: Carotid Artery Angioplasty And Stenting
Advanced Technology Radiology: Carotid Artery Angioplasty And Stenting The Mobile Age Is Upon Us
The Mobile Age Is Upon Us